What is a Paradoxical Effect?
Paradoxical effects and reactions are generally quite rare. They are described as experiencing the opposite of what a medication or drug is intended to do. It is an unusual medical response where the drug causes an effect that is opposite of what it would normally produce. For example, when a person uses Benadryl to treat allergies, it promotes sleep and sedation. During a paradoxical effect, a reaction to the drug causes hyperactivity, irritability and insomnia. The exact opposite of what the medication is supposed to do. The exact reasoning and science behind this phenomenon is still very unclear.

However, it is found to occur more frequently in medications that affect the central nervous system such as sedatives, stimulants, and psychoactive drugs. Substances such as benzos, barbiturates alcohol, propofol and inhaled anesthetics are commonly associated with paradoxical reactions. It is also more commonly seen in those who suffer from mental health disorders such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
There are three different types of paradoxical effects. One type of reaction occurs when a drug is prescribed for an explicit purpose. Another type of paradoxical response is a condition that can occur when the medication is being used in a different manner or for off-label purposes. The last type of paradoxical reaction that can occur can be an effect that is beneficial or adverse depending on various circumstances. Paradoxical reactions are unexpected outcomes as a result of medication or drug use and in some cases, can put patients at dangerous risk for health issues.
How do you know if you’re experiencing a Paradoxical Effect?
Some of the common features of a paradoxical effect or a reaction include experiencing emotional lability, agitation, excessive movement and confusion. It is also common to experience changes in autonomic activity including tachycardia and hypertension. Unfortunately, there is no uniform definition or uniform criteria that enables one to recognize when you might be experiencing a paradoxical effect or reaction.
Risk factors for developing a Paradoxical Effect
- Genetics
- Individual variation in metabolism – Each person processes drugs and medications at different speeds based on their own individual metabolism. In people who are sick or have damaged organs, this could mean a much slower processing rate because the organ is not functioning at full and healthy capacity. When this happens it could cause the medication to have a much stronger effect on the body.
- Brian chemistry
- Underlying health conditions
- Taking the wrong form of medication or interactions with other medications you are already taking – In some cases, you can develop a paradoxical effect by taking the wrong form of medication. For example, you have a vitamin C deficiency and taking the wrong form of vitamin C could affect how and if you are able to absorb the medication. When this happens, it can produce unintended side effects. The way your body processes medication is important.
- Taking too much or too little medication – In some cases, you might not be receiving the correct dose of the medication you need. It may be too little or too much. Often times people think more is better, but that is not always the case when it comes to prescription medications.
- Age – Paradoxical reactions are more likely to occur in young children and elderly adults because of their drug metabolism abilities and their central nervous system sensitivity.
Benzos and the Paradoxical Effect
Benzos are the most common class of medication that has been associated with users developing a paradoxical reaction. Benzodiazepines are a class of medication that is commonly used to treat conditions such as generalized anxiety, panic disorder and sleep disorders. They help suppress and sedate the central nervous system. Benzos can alter neurotransmitter concentrations of serotonin. This change in the central nervous system can contribute to increased feelings of agitation. Benzos drugs can cause cortical inhibition, which can contribute to violent behaviors that some people experience during a paradoxical reaction.
When on benzos medications, risk factors such as alcoholism, age, co-occurring mental health disorders, genetic predisposition and history of drug use can all contribute to the development of a paradoxical effect. Paradoxical reactions such as increased anxiety, agitation, hallucinations and hyperactive behaviors can occur when on benzos medications. In some cases, when a person experiences a paradoxical effect, they may try to self-medicate with more medication or other types of medication which only leads to an increased risk of developing a dependence and substance addiction.
Check Your Insurance Coverage for FREE
Find out if your insurance covers addiction treatment in minutes. We accept most insurance!
How to Manage a Paradoxical Effect
First and foremost it is extremely important to be able to recognize when you may be experiencing a paradoxical effect or reaction. It can be very difficult to identify. This is especially true for those who are physically dependent on benzos medications. Once you have, discontinue the drug immediately.
If not treated right away, it can lead to an increased dose of benzos or a worsening of the reactions of the drugs. In a medical and clinical setting, patients will receive immediate reassessment of their medication. It is possible that they will discontinue the use of medications or be changed to a substitution drug. Close monitoring will be performed for future paradoxical reactions. In some cases, the dosage of drugs may also be adjusted along with patient education on the side effects and importance of reported unusual reactions.
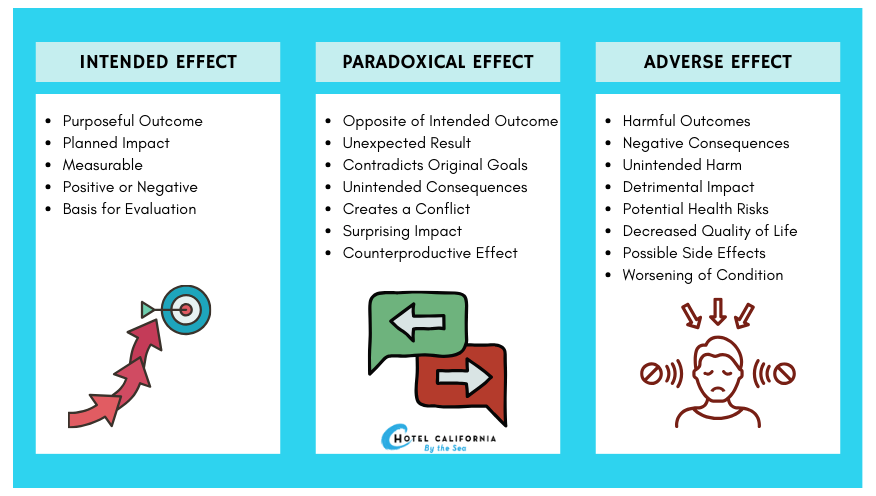
What are the differences between Paradoxical Effects, Adverse Effects and Side Effects?
Paradoxical effects can be similar to adverse effects. Despite the similarities, they are very different types of reactions. Paradoxical effects are a form of chemical reaction to using the drug. Adverse effects are unwanted or dangerous reactions to a drug or medication. It is an unintended consequence of a drug administration that can be both preventable and nonpreventable. Adverse drug reactions are either negative or irregular outcomes resulting from taking a certain type of medication.
Adverse drug reactions can be similar to side effects but they are always harmful and a negative consequence of using a drug. Defined by the World Health Organization, an adverse drug reaction is a response to a medication that is harmful and unintended. It can happen when taking a normal dose of medication during normal use. In other words, you can be taking your medication responsibly and still be a risk for an adverse drug reaction.
Adverse drug reactions can often imitate traditional diseases and disorders and can occur in all systems of the body. This can at times make it difficult to diagnose and pinpoint. There are two types of adverse drug reactions. Type A reactions are augmented reactions, in which they are dose-dependent and predictable due to the pharmacology of the drug. Type B reactions are bizarre reactions, which are not as predictable due to pharmacology. Fortunately, epidemiological studies have found that between 1/3 and 1/2 of adverse drug reactions are actually preventable.
When it comes to general side effects, it is defined as unintended, yet predictable symptoms that can develop while on a medication or drug. Side effects can occur even at the normal and recommended dose of medication. They are usually unrelated to the intended purpose of the prescribed medication. In some cases, side effects can even have beneficial outcomes. Examples of common side effects include drowsiness when using antihistamines, coughing when using blood pressure medications, weight gain while on antidepressants and some patients even see acne control with their medications.
Reach out to Hotel California by the Sea
We specialize in treating addiction and other co-occurring disorders, such as PTSD. Our Admissions specialists are available to walk you through the best options for treating your addiction.
Treatment for Substance Use Disorder
Medication used to treat disorders and conditions can be very helpful. However, it can also be very harmful. This is especially true when the patient experiences, paradoxical effects or develops an addiction to the medications. Behavioral health treatment programs such as Hotel California by the Sea, specialize in treating clients who have become dependent or addicted to substances.
We provide care throughout every stage of recovery including detox, residential, PHP and IOP. We utilize evidence-based treatment methods such as CBT, DBT and group therapy. We specialize in treating co-occurring mental health disorders and create individualized treatment plans for our clients. Hotel California by the Sea is dedicated to providing the tools, resources and support to help our clients overcome their addiction and live a healthier life in sobriety.
References:
https://comfortrecoveryllc.com/blog/paradoxical-effect-of-drugs
https://www.renaissancerecovery.com/paradoxical-effect
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2016/6748947
https://www.jneuropsychiatry.org/peer-review/adverse-effect-of-paradoxical-reaction.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6297296
https://www.goodrx.com/drugs/side-effects/vs-adverse-reaction
https://www.benzoinfo.com/paradoxical-reactions/