How to flush Alcohol out of your system
You’re out with friends and have had a few drinks or two. Somewhere along the way, those few drinks turn into too many drinks. How long will it take for the alcohol to leave your body? How do you flush alcohol out of your system? Scientifically speaking, if you are excessively drinking, but want to flush alcohol out of your body as quickly as possible, all you can do is wait. The human body is very efficient in processing alcohol. However, the processing system depends on many different factors including, how much you have drank, the type of alcohol you consumed, biological factors, environmental factors, as well as individual metabolism.

Excessive drinking of alcohol and other compulsive alcohol use behaviors often lead to alcohol use disorder. In other words, alcohol addiction. Some of the effects of alcohol abuse include relaxation, drowsiness, euphoria, mood changes, loss of inhibitions, impulsive behavior, poor coordination, slurred speech, nausea, vomiting, headache, diarrhea, blackouts and difficulty concentrating.
When drinking alcohol, the time in which it takes to be eliminated from the body can vary. Alcohol can remain detectable in urine between 12-48 hours after the last drink. It can remain detectable in hair for up to 90 days after the last drink. Each individual’s metabolism is different and affects how fast or slow alcohol is processed in the body.
How is alcohol processed in the body?
In general, the average person processes alcohol at a rate of about one standard drink per hour. Once alcohol is ingested, it enters the digestive system by traveling to the stomach and small intestine. It is then absorbed into the bloodstream. About 20% of alcohol is absorbed through the stomach. The remaining 80% of alcohol is absorbed through the small intestine and bloodstream. Once alcohol hits the bloodstream, it is transported throughout the entire body. This is the reason why alcohol is able to affect so many different organs and body systems.
An average of 90-98% of the alcohol that enters the body is metabolized, while the remaining will be removed from the body through sweat, urine and feces. Once the alcohol is absorbed into the bloodstream, it eventually makes its way into the liver where it is processed and eliminated from the body. Two main enzymes process alcohol metabolism in the liver. Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) metabolizes alcohol to create acetaldehyde. It is then further broken down to acetate and then into water and carbon dioxide to be easily eliminated from the body. Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) breaks down the majority of the alcohol consumed and converts it into energy. These two enzymes are primarily responsible for the alcohol processing in the liver.
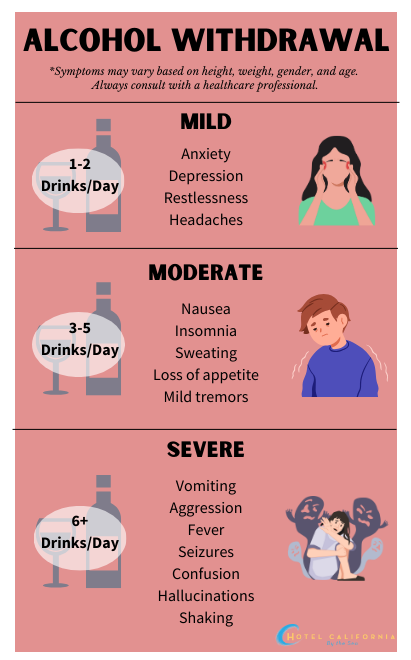
Alcohol Detox Timeline
Within the first 6-12 hours, symptoms of alcohol detox begin as mild and can quickly escalate to more moderate. Withdrawal symptoms include headaches, anxiety, shaking, nausea and irritability. After about 24 hours, withdrawal symptoms become increasingly severe and can include disorientation and seizures. During the second day of detox, serious symptoms will continue where you can experience hallucinations and panic attacks. On days 3-7, various withdrawal symptoms will come and go. This phase is also the most crucial for the risk of developing delirium tremens. After about a week, withdrawal symptoms will begin to taper off. The most serious side effect that can occur is post-acute withdrawal syndrome, in which you can experience prolonged symptoms of detox.
How to flush Alcohol out of your system
So how do you get alcohol out of your system? Like other substances you intake in your body, alcohol will leave your system naturally as it’s metabolized by the liver. Are there ways to help you metabolize alcohol faster or slower? No. But, there are various biological and environmental factors that can impact how the alcohol is processed in your body.
- Age – An older person will take longer to metabolize alcohol compared to a younger adult.
- Gender – It takes longer for females to process alcohol compared to their male counterparts. This is due to the biological make up of the female body.
- Food – Having food in the body will help slow down the alcohol absorption rate and can even help dilute some of the alcohol that is in the stomach.
- Body size – A person’s height and weight can affect how quickly alcohol is absorbed. A smaller person will tend to become intoxicated much faster than a person who is bigger.
- Medical Health – The health of your liver plays an important role in the metabolization of alcohol. A healthy liver will be able to effectively process alcohol at a normal rate. However, excessive drinking can slow down the processes and cause a build-up of alcohol toxins in the body.
- Genetics – Someone with a history of alcohol abuse in their family is more likely to develop unhealthy alcohol use behaviors.
- Medication and other substances – A person taking other types of medications or other substances can impact alcohol’s effects on their body.
Check Your Insurance Coverage for FREE
Find out if your insurance covers addiction treatment in minutes. We accept most insurance!
How is the amount of alcohol in the body measured?
The amount of alcohol in a person’s body is measured by blood alcohol concentration (BAC). This is the blood alcohol content and percentage of the alcohol within the bloodstream. A person with a BAC between .05% to .044% produces feelings of calmness, happiness and relaxation that can eventually turn into depression, irritability and disorientation. When the BAC reaches between .08% to .09%, the person’s sense of balance is off, they have impaired motor skills and may even begin to vomit due to the excessive levels of alcohol within the blood. This is because the body is unable to metabolize and process the alcohol fast enough in comparison to how much the person is consuming.
Factors that affect Alcohol metabolism
- Exercise – Exercising won’t directly increase the speed at which alcohol is processed. However, it can help improve overall metabolic function as well as liver health. This can help the metabolism process go more smoothly and efficiently in the long run, which may be able to create a faster metabolism in the future.
- Drinking water – Drinking water doesn’t help sober you up. It can help keep you hydrated, as alcohol is a diuretic. Staying hydrated can help your body to perform its functions properly and effectively.
- Diet – Eating nutritious foods can help boost the efficiency of metabolism and aid in the digestive system. Having a nutritious diet can indirectly help the body process alcohol better as it moves out of your system.
- Rest – Rest and plenty of sleep allow the body to heal and recover as it works to eliminate alcohol from your system.
Reach out to Hotel California by the Sea
We specialize in treating addiction and other co-occurring disorders, such as PTSD. Our Admissions specialists are available to walk you through the best options for treating your addiction.
Treatment for Alcohol Use Disorder
Alcohol use disorder is a common disease, affecting people worldwide. Elimination of alcohol from the body follows the same process as many other substances that are ingested into the body orally. There is no faster way to flush out alcohol. Although there are ways to make you feel more sober and possibly reduce the impact of unpleasant withdrawal symptoms from alcohol. Things such as drinking caffeine, drinking water, eating, or exercising can help you feel more sober. But it doesn’t necessarily mean the alcohol has been eliminated from the system.
Hotel California by the Sea provides alcohol use disorder treatment care for clients at all levels of their addiction. We offer detox, residential and outpatient treatment programs. We utilize evidence-proven treatments such as CBT, DBT and EMDR therapy to help our clients get to the root understanding of their addiction. Hotel California by the Sea is dedicated to providing the resources, support and tools clients need to overcome their addiction.
References:
https://www.alcoholrehabguide.org/alcohol/how-long-alcohol-stay-system
https://www.addictioncenter.com/alcohol/how-long-is-alcohol-in-your-system
https://www.alcoholrehabguide.org/treatment/alcohol-detox
https://www.sunnyside.co/blog/alcohol-metabolism
https://mandalahealingcenter.net/how-to-flush-alcohol-out-of-your-system/
https://www.addictiongroup.org/alcohol/in-your-system/
