What is the Difference between Stimulants and Depressants?
Some of the most addictive mind-altering substances can fall under two main categories of drugs: stimulants and depressants. These types of drugs interact with a person’s central nervous system and throw off the chemical balance of the body and brain producing both physical and psychological impact. Stimulants work by speeding up activity in the brain and body. Depressants work in the opposite and slow down physical functions and cognitive processing. There are in fact many different classifications of drugs. However, the two most commonly known types of addictive drugs are stimulants and depressants.
Different Classification of Substances
Some drugs are categorized by chemical make-up because they produce similar impacts and risks on the user. These drugs fall under the categories of alcohol, opioids, benzodiazepines, cannabinoids and barbiturates. They are grouped into these categories because treatment is often more effective for chemically similar substances.
Another type of drug classification is based on legal definitions. The legal classification of drugs is based on the perceived medical value of the substance along with its perceived risk of abuse and danger. These drugs are classified under the Controlled Substances Act. Schedule V controlled substances include Lyrica and Motogen. Schedule IV controlled substances include Ambien and Tramadol. Schedule III controlled substances include anabolic steroids, ketamine and Vicodin. Schedule II controlled substances include codeine, methadone and Ritalin. These types of drugs are highly regulated and have harsher penalties despite having legitimate accepted medical uses. Schedule I controlled substances include ecstasy and GHB and are regarded as the most regulated, have the heaviest penalties of any drug and have no legitimate accepted medical uses with a high potential for abuse.
The most common type of drug categorization is through drug effect. Drugs based on their effects fall into a few main categories including stimulants, depressants, hallucinogens or psychedelics, dissociatives, opioids, cannabinoids and inhalants.
What is abuse and misuse of substances?
- When you take a higher dose than prescribed or recommended
- When you take a dose more frequently than prescribed or recommended
- When you take someone else’s medication that isn’t yours
- When you mix stimulants and depressants with other drugs
- When you take stimulants or depressants with the sole intention of getting high
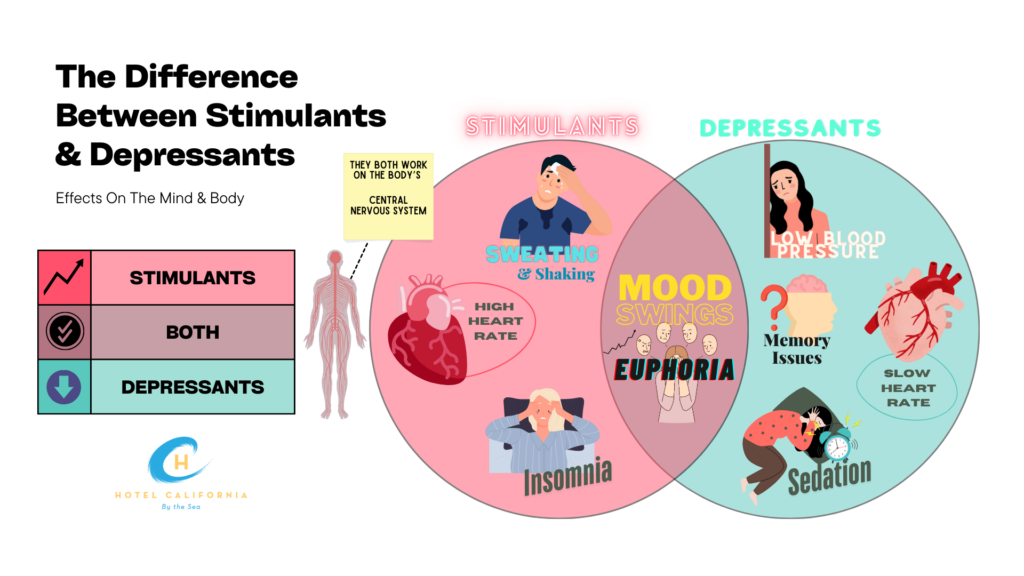
What is the difference between Stimulants and Depressants?
Stimulants
- Uppers – they impact the central nervous system by stimulating communication between the brain and body, making it more active and speed up body functions.
- Examples of stimulant drugs include – cocaine, MDMA, methamphetamine, amphetamine, Dexedrine, nicotine and caffeine.
- Prescription stimulants – Adderall, Ritalin, Concerta, Dextroamphetamine.
- Simulants increase the activity of brain chemicals dopamine and norepinephrine.
- Stimulants are usually prescribed to treat ADHD, narcolepsy, exogenous obesity, obstructive sleep apnea, fatigue disorders, OCD, acute stress, muscle spasms and sedation.
- According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, an estimated 5 million Americans misuse prescription stimulants every year and many of those lead to addiction.
- Stimulants make users feel more hyper-focused, have intense energy levels, awake, have improved reaction time, improved coordination and a sense of a rush also known as euphoria.
- Side effects of stimulant abuse include – decreased appetite, weight loss, increased blood pressure, constricted pupils, accelerated heart rate, paranoia, erratic heartbeat, seizure or convulsions, stroke, brain damage, coma, organ toxicity, cerebral hemorrhage, cardiovascular damage and GI damage.
- Psychological effects of stimulant abuse include – increased anxiety, paranoia, schizophrenia, depression and psychosis.
- Stimulants work by making users feel an intense sense of euphoria and energy followed by the same intense feeling of exhaustion and depression when they come off the high of the drug.
- High doses of stimulants can lead to overstimulation and trigger the development of anxiety disorder, panic attacks, seizures, tremors and the development of aggressive and violent behavior.
Depressants
- Downers – they inhibit the actions of the central nervous system by slowing down the heartbeat, and breathing and often make users feel calm, sedated and relaxed.
- Depressants increase the activity of the GABA neurochemical that inhibits brain activity and reduces arousal or brain stimulation.
- Depressants slow down the body’s natural response system and can impact coordination and cognitive functions such as concentration.
- Examples of depressant drugs include – alcohol, opiates and benzos. They can include both prescription drugs as well as illegal street drugs.
- Prescription depressants are usually used to treat conditions such as sleep disorders, OCD, PTSD and other mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
- There are four main types of depressant substances – barbiturates, benzodiazepines, sleep medications and alcohol.
- Benzodiazepines include Xanax, Klonopin, Valium and Ativan.
- Sleep medications include Lunesta, Ambien and Sonata.
- Alcohol is the most popular depressant drug and impacts the dopamine hormone.
- Side effects of depressant drug abuse include increased appetite, weight gain, lowered blood pressure, extreme relaxation, dilated pupils, slowed pulse, respiratory depression, difficulty concentrating, reduced reaction time, slurred speech and confusion.
- Depressant drugs pose a significant risk of drug abuse and dependency because they produce feelings of euphoria, which can be used as an unhealthy coping mechanism for users who are dealing with emotions, past trauma and underlying mental health conditions.
Check Your Insurance Coverage for FREE
Find out if your insurance covers addiction treatment in minutes. We accept most insurance!
What happens when you mix Stimulants and Depressants?
Many users participate in mixing stimulant and depressant drugs together in an attempt to achieve a greater or more intense high. They believe there is little danger as the drugs, which produce opposing effects, will eventually cancel each other out. It is a myth that mixing stimulants with depressants can cancel out each other’s effects. In fact, mixing both types of substances can lead to dangerous outcomes. It puts double the amount of strain and stress on the body when it’s being pulled from one extreme to another.
Stimulants are not likely to affect the respiratory system while depressants can greatly impact breathing and slow it down to the point where a person can stop breathing altogether. Stimulants produce high energy while depressants reduce energy. Stimulants provide motivation, while depressants reduce feelings of motivation. Stimulants can increase feelings of impulsive behaviors, while depressants struggle to push users to take any action at all.
The effects of mixing Stimulants and Depressants
- Oftentimes when mixing the two, users are unaware of the effects of the other drug. It can mask the effects of both drugs or just one drug. When the effects of one drug wear off, the effects of the other can unexpectedly kick in.
- When mixing the two, it can cause the user to take too much of one or both drugs. When the user is high on both, they can mask each other’s effect making the user assume they need more in order to feel something. This is dangerous and can easily lead to overdose.
- When mixing stimulants and depressants, can cause the creation of a toxic chemical. One example includes alcohol and cocaine, which produces coca ethylene, a highly toxic chemical.
- Both depressants and stimulant drugs can cause dehydration, which results in severe organ damage.
Reach out to Hotel California by the Sea
We specialize in treating addiction and other co-occurring disorders, such as PTSD. Our Admissions specialists are available to walk you through the best options for treating your addiction.
Treatment for Substance Use Disorder
Stimulant and depressant drugs are some of the most highly sought-after and highly addictive drugs with the capability of producing intense feelings of euphoria. Stimulants create an intense rush of excitement and euphoric pleasure, while depressants produce an intense level of relaxation, sedation and calming euphoria. These drugs produce effects on opposite ends of the spectrum, but can both be dangerous and deadly. An addiction to stimulants and depressants is best managed under a behavioral health treatment program such as Hotel California by the Sea.
Our programs specialize in treating addiction to stimulants and depressants. We offer treatment at every level of care including detox, residential, PHP and IOP. We utilize evidence-based treatment methods such as CBT, DBT, group therapy and family therapy. Hotel California by the Sea is dedicated to helping our clients achieve sobriety and overcome their addiction.
References:
https://www.addictioncenter.com/drugs/drug-classifications
https://thearbor.com/blog/the-difference-between-stimulants-and-depressants/
https://www.freedomaddiction.ca/blog/drug-categories-explained/
https://aod.rutgers.edu/get-facts/types-substances
https://addictionresource.com/drugs/stimulants/vs-depressants